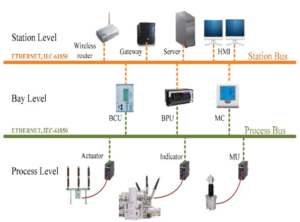
The Difference Between RPA and RDA
Robotic process automation has become a hot topic of discussion in the service space. People are excited, skeptical and curious about this new technology.
RPA is a dynamic tool that works well with ongoing processes. It can also reduce costs by eliminating the scope of additional human hires. It can run on a desktop or server and works without being instructed.
What is RPA?
RPA is a type of automation that uses software to perform tasks within a specific workflow. It works like a digital assistant for employees, freeing them up to focus on more important work and improve the customer experience. RPA eliminates tedious desktop tasks that many employees hate to do, such as copying and pasting information between applications or hunting through multiple windows for the same piece of data. This gives employees time to focus on more productive tasks and boosts employee satisfaction and morale.
Another benefit of RPA is that it can be deployed in a cloud-based environment (RPA as a service) or on virtual desktops, giving employees access to their solutions from anywhere they are working. RPA can also be accessed by non-technical users, which allows business leaders to take control of the software and avoid waiting for IT to get involved.
The main goal of RPA is to minimize human supervision in the overall process, which helps businesses save time and money while boosting productivity. However, there are a few things that should be considered before implementing RPA. First, it is important to identify the processes and tasks that need to be automated. This can include anything from data entry to customer service. Once the processes and tasks have been identified, it is then necessary to develop a plan for implementation. This can be done by creating a roadmap and setting clear expectations for the project team.
What is RDA?
RDA is a global library standards framework for descriptive and bibliographic data. It is a higher-level, more flexible framework that provides for more options for catalogers than the previous version of AACR2. RDA is based on linked data principles.
Robotic process automation (RPA) is a business software solution that automates tasks without human intervention, saving companies money on hiring employees. It can be used in a variety of ways, from streamlining workflow procedures to automating repetitive daily tasks. RPA can also be used to automate the task of logging into different systems and applications to retrieve information such as addresses and customer records.
It also improves the overall user experience by enabling employees to quickly solve queries for customers. This is because it removes the hassle of log-in screens and forms that slow down the time taken to resolve problems. It also reduces the need for employee training, as it is simple to use and does not require any coding knowledge.
Local cataloging agencies/communities have the flexibility to use RDA in the way they wish, through application profiles, policy statements, community vocabularies, etc. ALA Digital Reference supports these local decisions by making them freely available through the policies tab of the preview pane. These documents are not behind a paywall, and the ALA Digital Reference team has communication protocols and liaisons with other library standards organizations to ensure that RDA decisions can be shared.
What is the difference between RPA and RDA?
RDA and RPA are two technologies that can help to automate processes within your business, but they have different applications depending on the type of automation you need. For example, RPA is a software technology that uses cognitive technologies to automate back-office tasks for any industry that handles rules-based workflows. It can streamline departmental and individual tasks and free up your employees to focus on more value-driven work. For instance, your call center agents can focus on the most important customer needs rather than copy-pasting the same answers or navigating multiple windows to find information.
RPA also has a larger scope in terms of its ability to handle data-related processes. It can use AI to perform a number of actions such as data extraction, validation, metadata aggregation, and wrangling across disparate systems.
Unlike RPA, RDA does not require human intervention to carry out its automation. It can essentially act as a personal assistant that is triggered by specific events or by your employees’ behavior. For example, your employees can record and trigger their RDA system to automatically re-perform certain actions or fields that they fill out or repeat regularly.
For example, if you have an online shipping partner and your agents have to frequently check status updates on their website, your RDA solution could shave minutes off their time by opening that site in a new tab and pulling in the information without requiring any API integration with the partner. This enables your agents to give customers faster and more personal service.
What are the benefits of RPA and RDA?
Streamlining workflow procedures helps employees focus on what matters most—serving customers and meeting their needs. RDA and RPA can help streamline both departmental and individual tasks, freeing employees to focus on more important work.
While the benefits of RDA and RPA differ, they both allow businesses to reduce manual labor and time spent on repetitive processes. RPA focuses on automating the most complex tasks, such as processing orders and updating databases, while RDA is better suited for automated desktop-based tasks.
For example, Bernard Marr explains that an HR manager can create an automation that identifies application forms and resumes that need to be sent to other systems for archiving or sending a job offer letter. RDA can also automatically send these materials to internal IT systems and create new user accounts—all without human intervention.
RDA solutions are simple, lightweight and easy to customize for each desktop. They are often referred to as attended automation because they are triggered by events, such as a customer call or an email notification, and can only be activated at a specific desktop.
Smart RDA can also capture and analyze data to provide insights into customer behavior and company performance. This information can be used to improve operations and drive growth. By automating data collection and analysis, companies can eliminate error-prone manual steps, freeing up time for employees to focus on more value-add work.